- Visibility 26 Views
- Downloads 2 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijceo.2024.080
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Comparison of corneal ulcer size and depth measurement by slit lamp and anterior segment optical coherence tomography
Introduction
A corneal ulcer is defined as disruption in outer layer of cornea affecting the stroma beneath, poses a significant threat to vision and is contemplated an ocular emergency.[1] Even with prompt treatment, the patient may experience severe morbidity, such as anterior and posterior synechiae, corneal scarring or perforation, cataract, glaucoma and impairment of vision. If left untreated, infectious keratitis can lead to endophthalmitis and even blindness.[2] In the US, the annual prevalence of corneal ulcers is anticipated to be beyond tens of thousands, with approximately 12.2% of corneal transplants performed to manage infectious keratitis.[3]
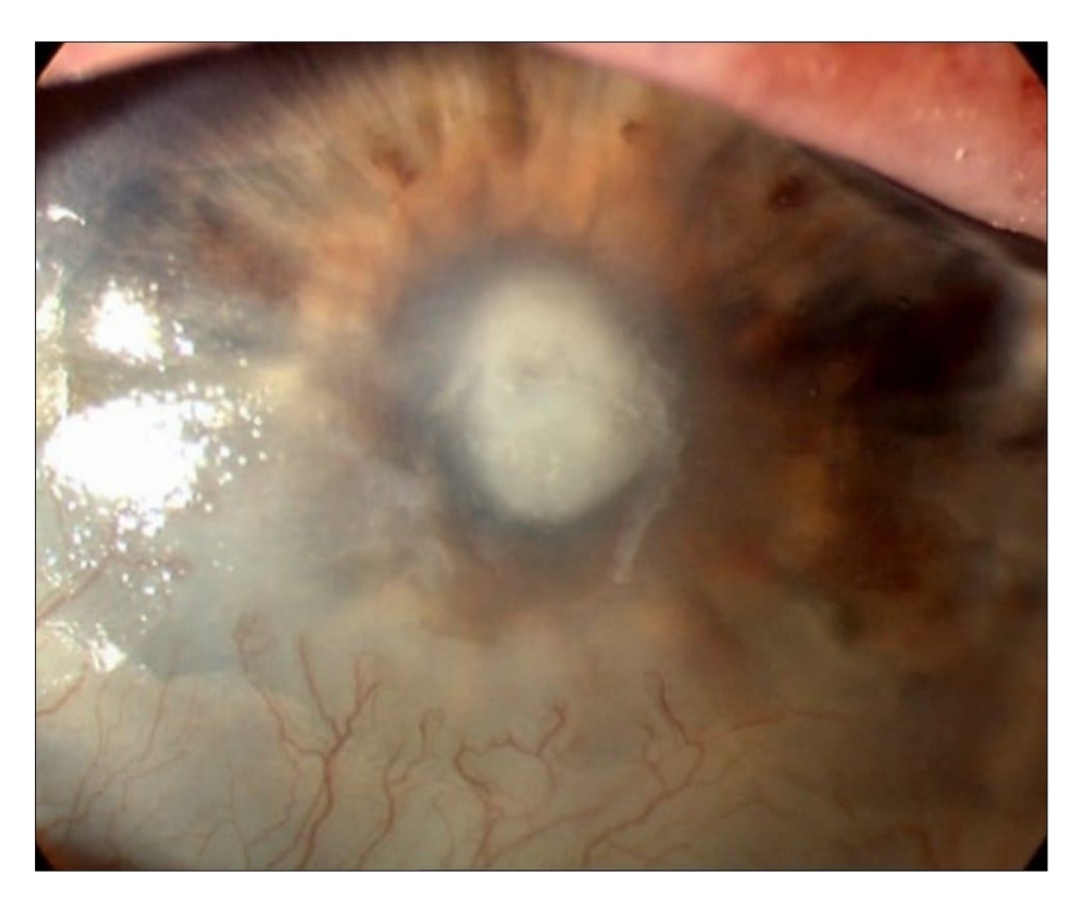
Corneal ulceration, may resolve without medical intervention, or may progress to perforation with serious consequences, or result in an opacity that can lead to vision loss if focal. The chronicity of is influenced by a combination of factors, including geographic and regional aspects, the level of development of the country, prevalent influencing factors, and the types of infections often found in the community.[4], [5]
Accurate measurement of corneal ulcers is essential for diagnosing the severity of the condition, monitoring progression, and assessing the efficacy of treatments. Traditionally, slit lamp biomicroscopy has been the primary method used by ophthalmologists for evaluating corneal ulcers. However, it has limitations, particularly in terms of accuracy and reproducibility. Measurements obtained from slit lamp examinations can vary significantly between different observers due to the subjective nature of the evaluation. Newer imaging approaches includingOptical coherence tomography (OCT) has demonstrated a great deal of promise for utilization. It has revolutionized clinical and surgical treatment of the cornea by improving understanding of corneal pathology. A non-contact, in vivo ocular imaging technology called AS-OCT uses low-coherence interferometry to determine the echo time lag of light scattered back from tissue organization. It combines numerous axial scans to create a composite B-scan picture.[6]
A number of corneal diseases have been studied by AS-OCT, including keratitis, ectatic disorders, corneal dystrophies and degenerations, and ocular surface disorders. Additionally, it is helpful for ocular trauma, keratoplasty, and refractive surgery’s planning prior to surgery and during recovery. Although the Principal diagnosis of these conditions is clinical, AS-OCT is beneficial in cases with subtle or subclinical trait. Additionally, OCT can quantify corneal changes, aiding in the grading of disease graveness and keeping track of progression.[6]
This study aimed to explore the correlation between the size and depth of corneal ulcers measurements utilizing SLIT LAMP and Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography.
Materials and Methods
A hospital-based, prospective, non-randomized, observational clinical study conducted in the Department of Ophthalmology at Hind Institute of Medical Sciences, Safedabad, Uttar Pradesh over the duration of 18 months.
After taking clearance from ethical committee, 100 subjects were recruited&written informed consentwere obtained.
Inclusion criteria
New diagnosed cases of corneal ulcer that occurred before corneal scraping.
Corneal ulcers of diverse sizes.
Patients willing to participate in the study.
Aged 16 years and above till
Exclusion criteria
Perforated ulcers.
Ulcers with impending perforation.
Total corneal ulcers.
Non-infective ulcers such as Mooren's ulcer and Shield's ulcer.
Past corneal surgery performed on the affected eye.
Acuity of vision less than 3/60.
Patients with ages under 16.
Women who are expecting.
Patients who refuse to participate.
Sample Size
100 subjects recruited for the study.
Formula:
Adequate sample size was calculated by using the formula
N = Z2α p (1-p) / E2
Where, p – Proportion or prevalence or incidence
Zα- Critical value of standard normal variate at α level of significance
E- Margin of error or Allowable error
E- 10% = 0.1 (Absolute margin of Error)
n – (1.96)2 x 0.468 (1-0.468)/ (0.1)2 = 95.6
N = 96 (Sample Size)
Thus total sample size taken as 100.
Methodology
The patient was recruited from Ophthalmology OPD, Hind hospital. After documenting the detailed history and ocular examination of the patient, the following clinical examination steps were taken-
Visual Acuity (UCVA) using Snellen’s chart at 6 mts
Corneal ulcer was initially evaluated n slit lamp Biomicroscopy, prior and post staining with Fluorescein dye, before the corneal scraping, and the findings were measured.
Following slit lamp evaluation, the ulcer size was measured using Appasamy SD-OCT.
Parameters were measured and the final value was considered for the interpretation of the results.
The parameters measured in the anterior segment OCT were maximum vertical diameter (length), maximum horizontal diameter (breadth), depth of the infiltrate and corneal thickness at the point of maximum infiltration.
Data collection
Individual interviews and thorough ocular evaluations of the individual were used to collect the principal data in accordance with the study protocol.
A thorough database was then created by entering the gathered data into Microsoft Excel sheet.
To compare with the principal data, secondary data were also obtained from a variety of publications and papers, PubMed, and Cochrane.
Statistical analysis
Results were analyzed as frequencies, percentages, and mean ± SD.The Paired t-test was used to compare continuous variables.The Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated.A p-value of less than 0.05 was contemplated significant.All analyses were performed availing SPSS version 16.0 (Chicago, Inc., USA). The statistical Analysis was done using SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science) Version16.0 Statistica Analysis Software. The values were represented in Number (%) and Mean ± SD.
Results
This study set out to compare the reliability of slit lamp evaluation and indigenous anterior segment optical coherence tomography in determining the size and depth of corneal ulcers at the Hind Institute of Medical Sciences' Department of Ophthalmology. In all, 100 patients were enrolled in the research.
More than one third of patients were between 51-60 years of age (37%), 41-50 (23%), <30 (22%) and 30-40 &>60 (9%) years. The mean age of patients was 45.74±13.61 years ranging from 22 to 78 years. Majority of patients were males (75%). Right eye was involved among more than half of patients (65%) followed by left eye (35%). ([Table 1])
The length of infiltrate was remarkably (p=0.001) lower by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method observed by both the observers. The breadth of infiltrate was remarkably (p<0.05) higher by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method observed by both the observers. The depth of infiltrate was remarkably (p=0.001) lower by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method observed by both the observers. No significant (p>0.05) difference was seen in the measurement of length, breadth and depth of infiltrate by SLIT LAMP and ASOCT methods between both the observers. ([Table 2])
Corneal thickness measured by ASOCT was remarkably (p=0.04) lower evaluated by observer 1 (637.76±135.26) than observer 2 (640.66±130.16). ([Table 3]) Highly significant positive (p=0.0001) correlation was found between SLIT and ASOCT in all the measurements evaluated by both the observers. ([Table 4])
|
|
|
No. (n=100) |
% |
|
Age in years |
<30 |
22 |
22.0 |
|
30-40 |
9 |
9.0 |
|
|
41-50 |
23 |
23.0 |
|
|
51-60 |
37 |
37.0 |
|
|
>60 |
9 |
9.0 |
|
|
Mean±SD (Range) |
45.74±13.61 (22-78) |
|
|
|
Gender |
Male |
75 |
75.0% |
|
Female |
25 |
25.0% |
|
|
Eye involved |
Left |
35 |
35.0% |
|
right |
65 |
65.0% |
|
|
|
SLIT LAMP |
ASOCT |
p-value1 |
|
Length of infiltrate |
Observer 1 |
4.08±2.27 |
4.27±2.06 |
0.001* |
|
Observer 2 |
4.08±2.27 |
4.24±2.07 |
0.001* |
|
|
p-value1 |
1.00 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
Breadth of infiltrate |
Observer 1 |
7.52±0.86 |
7.44±0.59 |
0.02 |
|
Observer 2 |
7.51±0.87 |
7.45±0.55 |
0.03 |
|
|
p-value1 |
0.92 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
Depth of infiltrate (%) |
Observer 1 |
29.01±12.04 |
33.14±13.62 |
0.001 |
|
Observer 2 |
29.56±11.59 |
33.77±13.73 |
0.001 |
|
|
p-value1 |
0.15 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
Corneal thickness (Mean±SD) |
|
Observer 1 |
637.76±135.26 |
|
Observer 2 |
640.66±130.16 |
|
p-value1 |
0.04* |
|
|
Observer 1 |
Observer 2 |
||
|
Correlation coefficient |
p-value1 |
Correlation coefficient |
p-value1 |
|
|
Length of infiltrate |
0.97 |
0.0001* |
0.97 |
0.0001* |
|
Breadth of infiltrate |
0.97 |
0.0001* |
0.79 |
0.0001* |
|
Depth of infiltrate |
0.96 |
0.0001* |
0.92 |
0.0001* |
Discussion
An essential component of ocular examination is the assessment of the anterior segment. Traditionally, a slit lamp and gonioscope are used to assess the anterior segment and iridocorneal angle. Technology progressed to the point that low coherence interferometry was created, which served as the foundation for optical coherence tomography (OCT). OCT offers several fine-grained cross-sectional pictures of biological tissue’s interior architecture. OCT has gained notoriety as a vital tool for the diagnosis and treatment of several corneal and anterior segment conditions, delivering a thorough assessment in a safe and non-contact manner. At present there are two anterior segment (AS-OCT) models in the market the slit-lamp OCT and the Visante OCT. Non-invasive investigation of the anatomy and the diseases of the Anterior segment have been made feasible since the availability of these two models.[7]
According to Shousha MA et al (2013)[8] there is a strong agreement between the results of histology and AS-OCT in cases with ocular surface lesions, suggesting that AS-OCT probably be put to be used as an additional examining instrument. Histological diagnosis is difficult to obtain in patients with peripheral ulcerative keratitis (PUK) (Ladas and Mondino, 2000).[9] With a resolution of 1um/pixel, confocal microscopy may also be useful for studying epithelial cells and stromal keratocytes since it may provide pictures similar to those obtained from histochemical approaches (Hernandez-Quintela E et al, 1998).[10]
Above one-third of the patients in this research were between the ages of 51 and 60 (37%), followed by those between the ages of 41 and 50 (23%), <30 (22%) and 30-40 & above 60 (9%). Patients varied ranging in age from 22 to 78 years, with a 45.74±13.61 year mean. The age range of the patients in the Konstantopoulos A et al (2011) 11 study was 21 to 80 years old, with a mean age of 48.4. In a follow-up study, Uyar E et al. (2022) 12 discovered that the mean age was 35.8±11.0 years. Bonnet C et al. (2020)13 report that the patients' ages ranged from 33 to 74 years old, with a mean diagnostic age of 50.3 sd 14.7 years. According to Tawfeek M et al (2023),[11] the mean age of the patients was 42.8 sd 8.35years.
Majority of patients were males (75%) in the current study while as the study done by Konstantopoulos A et al(2011)[12] found that half of patients were males (50%), Uyar E et al (2022)[13] reported that out of 63 patients, 96.8% of the patients were men. In the study by Bonnet C et al (2020),[14] out of 6 eyes of 6 patients, there were 4 women (66.7%) and two men (33.3%). of the 17 patients who were included in the Chaturvedi I et al (2021),[15] 11 were female and 6 were male this study found that right eye was involved among more than half of patients (65%) followed by left eye (35%). Similar to the attending study, Konstantopoulos A et al (2011)[12] also found that right side eye was involved among more than half of patients (69.2%).
In the current study, the breadth of infiltrate was notably (p<0.05) higher by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method observed by both the observers. When measuring the breadth of infiltration using the SLIT LAMP and ASOCT techniques, there was no significant difference (p>0.05) observed between the two observers. The SLIT LAMP method significantly (p=0.001) reduced the infiltration depth compared to the ASOCT method that both observers noticed. The depth of infiltrate was notably (p=0.001) lower by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method observed by both the observers. There was no significant (p>0.05) dissimilarity in the measurement of depth of infiltrate by SLIT LAMP and ASOCT methods between both the observers. According to AS-OCT measurements, the mean depth and breadth of the corneal wounds in the study by Uyar E et al (2022) [13] were 117.0+/-42.5 and 332.9+/-99.4um, respectively. 18.9+/-6.1% was the mean percentage of corneal wound depth. Over the course of the two months, it was noted that in 20 patients who showed up for follow-up, the diameter of the incision widened and the thinnest stromal thickness at the wound site shrank. According to Patel TP et al (2018)[16] the interobserver consistency (ICC) of ophthalmologists measurements with SL calipers ranged from 0.84 to 0.88. The ICC range for SAS measurements was 0.96-0.98. According to Parikh PC et al (2017), [17] cornea specialists measured epithelial abnormalities in controlled, artificial setting with high reproducibility. In a non-trivial number of instances (31% to 52%), cornea experts disagreed in measuring length by >0.5mm, regardless of the method used.

This study found that corneal thickness measured by ASOCT was notably (p=0.04) lower evaluated by observer 1 (637.76±135.26) than observer 2 (640.66±130.16). In the attending study, there was high significant positive (p=0.0001) correlation between SLIT and ASOCT in all the measurements evaluated by both the observers. The mean IT and mean CT in the infiltrated region were both thickest at attendingation (710.88um and 288.76um respectively), according to Chaturvedi I et al (2021).[15] On days 3, 7, 14, 28 and 6 weeks, the mean CT shrank to 665.12um, 650.24um, 584.35um, 549um, and 507.47um in that order. In a similar study, the mean IT dropped to 154.82um, 197um, 244.41um and 287.24um. The study concluded that AS-OCT might display the morphological traits of infectious keratitis and provide a quantitative evaluation at each subsequent visit. Bonnet C et al (2020)[14] reported that the mean total CT at when the patient came at last follow up was significantly thicker (509+/-147um) on AS-OCT than it was at the outset (408+/-131um;P=0.03). The mean stromal thickness did not differ statistically (433+/- 130um at the final follow-up vs. 399+/-126um at commencement, P=0.62) when measured at the thinnest point, the epithelium was sometimes non-existent owing to an epithelial defect, hence the epithelial thickness was often not quantifiable at start.
Hsiao CH et al (2011)[18] discovered that in a single instance of Alternaria Keratitis, the central corneal thickness dropped from 584um to 532um in the only quantitative investigation on fungal keratitis. According to Chaturvedi I et al. (2021),[15] after three days after beginning therapy, there was a drop in CT in eight instances and andecrease in IT in eleven cases out of 13 cases of fungal keratitis.
The total daily decrease in CT and IT of Fungal Keratitis was 1.09% (p<0.0001) and 0.67% (p <0.0001) over the course of six weeks. In two instances of disciform keratitis Hsiao CH et al (2011)[18] discovered that in a single instance of Alternaria Keratitis, the central corneal thickness dropped from 584um to 532um in the only quantitative investigation on fungal keratitis. According to Chaturvedi I et al (2021),[15] after three days after beginning therapy, there was a drop in CT in eight instances and decrease in IT in eleven cases out of 13 cases of fungal keratitis.
The study population was limited to a specific geographic area, potentially impacting the applicability of results to broader populations. Some processes in the study still rely on manual input, which may introduce variability and human error.
Conclusion
This study showed the length and depth of infiltrate was significantly lower by SLIT LAMP than ASOCT method however the breadth of the infiltrate measured was higher by SLIT LAMP than AS-OCT. The overall corneal thickness measured was also found to be high when measured with AS-OCT. AS-OCT provides accurate and non-invasive measurements of corneal ulcer depth, which is not possible with slit lamp biomicroscopy. The use of AS-OCT as an adjunctive modality can enhance diagnosis and management of corneal ulcers. This study highlights the utility of AS-OCT in monitoring disease activity and providing valuable imaging guidelines for clinicians.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- F Ahmed, RJ House, BH Feldman. Corneal Abrasions and Corneal Foreign Bodies. Prim Care 2015. [Google Scholar]
- A Lin, MK Rhee, EK Akpek, G Amescua, M Farid, FJ Garcia-Ferrer. Bacterial Keratitis Preferred Practice Pattern. Ophthalmology 2019. [Google Scholar]
- S Sharma. Keratitis. Biosci Rep 2001. [Google Scholar]
- YW Ibrahim, DL Boase, IA Cree. Factors affecting the epidemiology of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2007. [Google Scholar]
- MJ Bharathi, R Ramakrishnan, R Meenakshi, C Shivakumar, DL Raj. Analysis of the risk factors influencing to fungal, bacterial & Acanthamoeba keratitis in south India. Indian J Med Res 2009. [Google Scholar]
- N Gupta, A Varshney, M Ramappa, S Basu, V Romano, M Acharya. Role of AS-OCT in Managing Corneal Disorders. Diagnostics 2022. [Google Scholar]
- H Li, V Jhanji, S Dorairaj, A Liu, DS Lam, CK Leung. Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography and its Clinical Applications in Glaucoma. J Curr Glaucoma Pract 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MA Shousha, CL Karp, AP Canto, K Hodson, P Oellers, AA Kao. Diagnosis of ocular surface lesions using ultra-high-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2013. [Google Scholar]
- JG Ladas, BJ Mondino. Systemic disorders associated with peripheral corneal ulceration. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2000. [Google Scholar]
- E Hernández-Quintela, F Mayer, P Dighiero, B Briat, M Savoldelli, JM Legeais. Confocal microscopy of cystic disorders of the corneal epithelium. Ophthalmology 1998. [Google Scholar]
- M Tawfeek, S Fouda, E Shahien, M Atia. Correlation between slit lamp (SL) examination and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) for the evaluation of central infectious corneal perforation. Zagazig Univ Med J 2023. [Google Scholar]
- A Konstantopoulos, G Yadegarfar, M Fievez, DF Anderson, P Hossain. In vivo quantification of bacterial keratitis with optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011. [Google Scholar]
- E Uyar, F Sarıbaş. Evaluating Depth and Width of Corneal Wounds Using Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography After Foreign Body Removal. Semin Ophthalmol 2022. [Google Scholar]
- C Bonnet, L Debillon, S Al-Hashimi, F Hoogewoud, D Monnet, JL Bourges. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography imaging in peripheral ulcerative keratitis, a corneal structural description. BMC Ophthalmol 2020. [Google Scholar]
- I Chaturvedi, K Singh, J Rana, K Dwivedi, R Sachan. Role of anterior segment optical coherence tomography in the evaluation of microbial keratitis. Indian J Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2021. [Google Scholar]
- T P Patel, N V Prajna, S Farsiu, N Valikodath, L M Niziol, Lakshey Dudeja. . Novel Image-Based Analysis for Reduction of Clinician-Dependent Variability in Measurement of the Corneal Ulcer Size 2017. [Google Scholar]
- P C Parikh, N Valikodath, C B Estopinal, R M Shtein, A Sugar, L M Niziol. . Precision of Epithelial Defect Measurements 2017. [Google Scholar]
- C H Hsiao, L K Yeh, H C Chen, H C Lin, Phil, David. Clinical Characteristics ofAlternariaKeratitis. Journal of ophthalmology 2014. [Google Scholar]
