Introduction
Corneal endothelium plays a crucial role in the maintenance of corneal transparency. Abnormality of corneal endothelium in quantity or quality might lead to bullous keratopathy, or decompensation of corneal endothelium. It is well-known that traditional cataract surgery, either phacoemulsification or extra capsular cataract extraction, causes damage to the corneal endothelium due to the manipulations in the anterior chamber1, 2, 3, 4 and it was believed by many surgeons that severely abnormal corneal endothelium was a relative contraindication to cataract surgery.
Pars plana lensectomy (PPL) is another technique of cataract surgery which extracts the cataractous lens from the vitreous cavity. This technique is able to avoid the manipulations in the anterior chamber and hence may decrease surgically-induced damage to the corneal endothelium. PPL is often performed to extract dislocated lens,5 or as a procedure during combined cataract and vitreo-retinal surgery,6 or on pediatric cataract patients.7 Encouraged by the good results, we introduced PPL to manage cataract with severely abnormal corneal endothelium from October 2018. This study comprised of 22 patients with severely abnormal corneal endothelium but still had transparent cornea, who underwent PPL as the technique of cataract extraction.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective analysis of 22 consecutive patients who had cataract with severely compromised corneal endothelium but still transparent cornea, and received PPL as the technique of cataract extraction was conducted. Of the 22 cases, 14 had history of penetrating keratoplasty, 6 had history of trabeculectomy and 2 were diagnosed as Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy before surgery. Preoperative examination included anterior segment evaluation by slit lamp, posterior segment evaluation by slit lamp biomicroscopy using either super vitreo-fundus lens, when fundus could be viewed, or by B-scan ultrasonography when media opacity blocked the viewing of fundus. Preoperative cell count of their corneal endothelium was between 844 to 1176 cells/mm2. To prevent postoperative retinal detachment, the peripheral fundus was paid special attention laser photocoagulation was conducted if there were any retinal breaks orlattice degeneration. The density and morphology of corneal endothelial cells were found using SP-3000 specular biomicroscope. All the patients received pars plana vitrecomy (PPV) and PPL, combined with phacofragmentation in 6 eyes because of hard nucleus, retinal photo coagulation in 7 eyes and CF temponade in 8 eyes to prevent retinal complications, primary intraocular lens (IOL) implantation in 1 eye and secondary IOL implantation in 4 eyes.
Surgical technique
The procedure of PPL was performed with PPV under retrobulbar or peribulbar anesthesia with maximal mydriasis. Three small conjunctival flaps and accordingly three 20G scleral ports were made 3.5 mm behind the limbus at the position of 2 and 10 o’clock and inferiotemporally. The inferiotemporal port was connected with irrigation, the 2 o’clock port was used for illumination, and the 10 o’clock port for vitrectomy, lensectomy, photocoagulation, etc. Anterior vitrectomy was performed to remove the nearby vitreous. With the vitreous cutter, a 5 mm×5mm opening of posterior capsule was made. If the nucleus was soft, a deep groove of nucleus was made from behind. The nucleus was then pushed down into the vitreous cavity, usually turned into two halves at this time. The remaining cortex behind the anterior capsule was aspirated and the epithelial cells on the posterior surface of the capsule were removed with the cutter by means of low-vacuum polishing. A plano-concave lens was placed on the cornea for better viewing of the posterior vitreous cavity. The nucleus was then removed half by half using the vitreous cutter. If the nucleus was hard, a phacoemulsifier was used to remove the hard nucleus in the vitreous cavity by means of phacofragmentation. A thorough fundus examination was conducted, with particular attention paid to the peripheral retina. Retinal photocoagulation, C3F8 tamponade was performed whenever there might be any risks for retinal detachment. Finally, the three scleral ports were closed by one stitch respectively using 6-0 absorbable suture. IOL implantation, either primary or secondary, was performed using a 3.0 mm corneo-scleral tunnel incision. Viscoelastic agent was injected into the anterior chamber and between the iris and the capsule. IOL was injected in with a projector and was fixed in sulcus. Viscoelastic agents were then carefully washed out by a cannula tip to avoid damage to the corneal endothelium.
Results
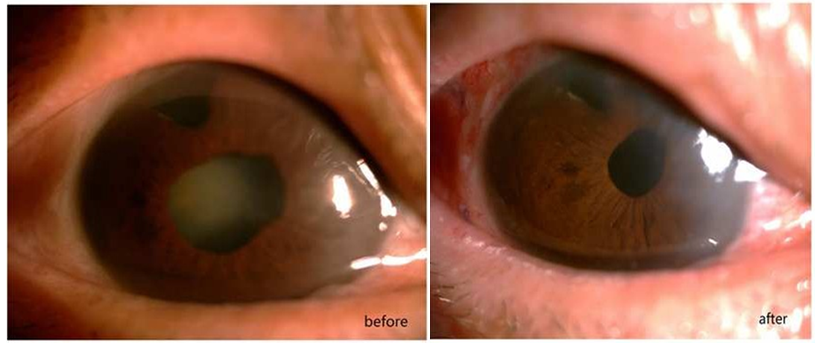
Between October 2018 and September 2020, 22 consecutive patients of cataract with severely abnormal/compromised corneal endothelium but still transparent cornea received PPL as the technique of cataract extraction. Twenty two eyes of 22 patients were enrolled in the study. The mean age of the 9 women and 13 men was 50.8 years ±12.5 (SD) (range 21 to 72 years). Mean follow-up was 17.2±6.4 months (ranged 6 to 31 months). Preoperatively, BCVA was PL present in 3 patients, FC in 4 patients, all below 6/60. Postoperative BCVA was 6/60 or below in 2 patients, 6/60-6/18 in 7 patients, 6/18 - 6/12 in 7 patients and 6/12 or better in 6 patients. BCVA improved in all patients after surgery, but in one patient with Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy BCVA turned worse again about five months after surgery and eventually bullous keratopathy occurred. She was then transferred to cornea specialist and received penetrating keratoplasty. The mean density of corneal endothelial cells was 1018± 84/ mm2 (range 844/ mm2 to 1176/ mm2) before operation and 981±93/ mm2 (range 853 to 1211/ mm2) after operation (Fig 1). No significant difference in the density of corneal endothelial cells was found among the patients before and after operation (P=0.43). Postoperative complications are shown in Table 1. Anterior capsule opacification developed in 10 patients, of which 8 had Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy and 2 had surgical capsulotomy at the time of secondary IOL implantation. BCVA improved and cornea remained transparent after capsulotomy in all patients. Bullous keratopathy occurred in one female patient with Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy. Her BCVA remained 6/6 for aproximately five months after PPL and then turned worse because of corneal edema. She therefore received penetrating keratoplasty and regained BCVA of 6/12.No patient had obvious uveitis on slitlamp examination, and none had retinal detachment (Figure 2).
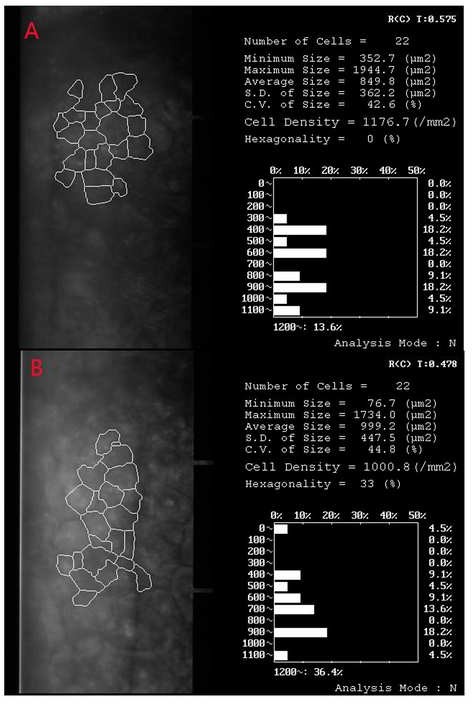
Figure 1
Density of corneal endothelial cells before (A) and 5 days after surgery (B) in a patient who had the history of trabeculectomy and received PPL as the technique of cataract extraction
Discussion
Corneal endothelium is a hexagonal non-replicating monolayer of neural crest–derived tissue that regulates the hydration state of corneal stroma. It’s a tissue that contains large quantities of membrane-bound Na+, K+-ATPase with specialized intercellular junctions that establish a pump–leak process in the maintenance of corneal deturgescence, and thus plays a crucial role in keeping the cornea transparent. Certain density and proper morphology of endothelial cells are important to maintain this function. This delicate tissue is, however, subject to alteration from age, trauma, systemic or ocular diseases, surgery and some dystrophic conditions. Because of the non-replicating propriety, repair of the damaged areas takes place via the process of cell migration from adjacent undamaged areas. Thus, a permanent reduction in cell density occurs, and individual cell size is increased. When the cell density drops beneath a threshold, the endothelium would no longer be able to work properly, and permanent cornea edema or bullous keratopathy occurs. We usually take corneal endothelial cell density of 1200 cells/mm as the threshold. Beneath the threshold, traditional cataract surgery should be carefully considered. The fast development of PPV has promoted PPL, which extracts the cataractous lens from the vitreous cavity, as a technique of cataract surgery. This technique is able to avoid the manipulations in the anterior chamber, and hence may decrease surgically-induced damage to the corneal endothelium. Although it is not a routine cataract surgery at present because of some severe complications such as retinal detachment and macular interference, PPL is often performed to extract dislocated lens5 or as a procedure during combined cataract and vitreo-retinal surgery6 or on pediatric cataract patients.7 It was based on two points that we introduced PPL into the management of cataract with severely abnormal corneal endothelium. Firstly, although few studies had reported the influence of PPL on corneal endothelium in the literature, theoretically however, this influence would be much less than that of phacoemulsificaion or extracapsular cataract surgery. Secondly, modern PPV had decreased the complications of PPL into a receivable level. Excellent visualization, high-speed cutting and prophylactic photocoagulation had greatly reduced the retinal and macular complications. Our present study showed this technique is promising. Of the 22 cataract patients who had received PPL because of severely abnormal corneal endothelium, only one had bullous keratopathy. Because the complication occurred five months after surgery, we would rather think that this represent the natural course of gradual deterioration of Fuch’s endothelial dystrophy. This study, however, was based on a small sample. More patients should be observed to further determine the influence of PPL on the corneal endothelium. The prominent complication of PPV in our study was anterior capsule opacification, with a prevalence rate of 47.6%. Compared with the posterior capsule, the anterior capsule possesses a monolayer of epithelial cells on its inner surface. This might account for the high prevalence of anterior capsule opacification. Capsule opacification can be managed by one of two methods: prophylactic capsulotomy intraoperatively or Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy post operatively. To further reduce anterior chamber interference, the latter was selected in our study. No patient had developed bullous keratopathy after Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy.